OBESITY & WEIGHT MANAGEMENT PROGRAMME
What is Obesity
Obesity is a complex disease involving an excessive amount of body fat.
Obesity isn’t just a cosmetic concern. It’s a medical problem that increases the risk of other diseases and health problems.
Effects on health
Obesity is correlated with various diseases and conditions, particularly cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, obstructive sleep apnea, certain types of cancer, and osteoarthritis.
High BMI is a marker of risk, but not proven to be a direct cause, for diseases caused by diet, physical activity, and environmental factors.
A reciprocal link has been found between obesity and depression, with obesity increasing the risk of clinical depression and also depression leading to a higher chance of developing obesity.

Mortality
Obesity is one of the leading preventable cause of death worldwide. A number of reviews have found that mortality risk is lowest at a BMI of 20–25 kg/m2 in non-smokers and at 24–27 kg/m2 in current smokers, with risk increasing along with changes in either direction.
Morbidity
Obesity increases the risk of many physical and mental conditions. These comorbidities are most commonly shown in metabolic syndrome.
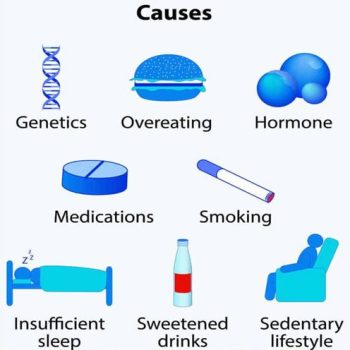
Causes
The “a calorie is a calorie” model of obesity posits a combination of excessive food energy intake and a lack of physical activity as the cause of most cases of obesity. A limited number of cases are due primarily to genetics, medical reasons, or psychiatric illness. In contrast, increasing rates of obesity at a societal level are felt to be due to an easily accessible and palatable diet, increased reliance on cars, and mechanized manufacturing.
- Diet
- Sedentary lifestyle :-
A sedentary lifestyle plays a significant role in obesity
- Genetics
- Other illnesses :-
Certain physical and mental illnesses and the pharmaceutical substances used to treat them can increase risk of obesity.
- Gut bacteria :-
Gut flora has been shown to differ between lean and obese people. There is an indication that gut flora can affect the metabolic potential. This apparent alteration is believed to confer a greater capacity to harvest energy contributing to obesity.
- Other factors :-
A number of reviews have found an association between short duration of sleep and obesity.
Management
- The main treatment for obesity consists of weight lossvia calorie restricted dieting and physical exercise. Dieting, as part of a lifestyle change, produces sustained weight loss, despite slow weight regain over time.
- Intensive behavioral interventions combining both dietary changes and exercise are recommended.
- Intermittent fasting has no additional benefit of weight loss compared to continuous energy restriction.
- Adherence is a more important factor in weight loss success than whatever kind of diet an individual undertakes.
Dietary Management
- Eat a diet lower in saturated and trans
- Include lots of fruits, vegetables, beans, nuts, whole grains, and fish regularly into your diet.
- Limit red meat and processed meats like bacon, sausage, and cold
- Maintain a weight that’s healthy for



